SUSTech Xiaofei Chen's group publishes latest research results of geophysical exploration in East Antarctic
22/09/2021
Recently, the research group of Professor Xiaofei Chen from the Department of Earth and Space Sciences at the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) published two geophysical exploration results on the East Antarctic region. The first paper, entitled “Measurement of ice flow velocities from GPS positions logged by short-period seismographs in East Antarctica,” was published in Science China-Earth Sciences. The second paper, entitled “Imaging the ice sheet and uppermost crustal structures with a dense linear seismic array in the Larsemann Hills, Prydz Bay, East Antarctica,” was published in Seismological Research Letter.

During the 36th Chinese National Antarctic Research Expedition (CHINARE36) in 2019/2020, Dr. Lei Fu deployed 100 short-period three-component seismometers (SmartSolo-BD3C-5) in the Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica, and acquired ~2 TB seismic noise data. Prof. Chen’s team have carried out related researches, including ice sheet velocity measurement, imaging of the ice sheet and upper crust structure, and ice-quake activity of Dalke Glacier, based on the recorded ambient noise data.
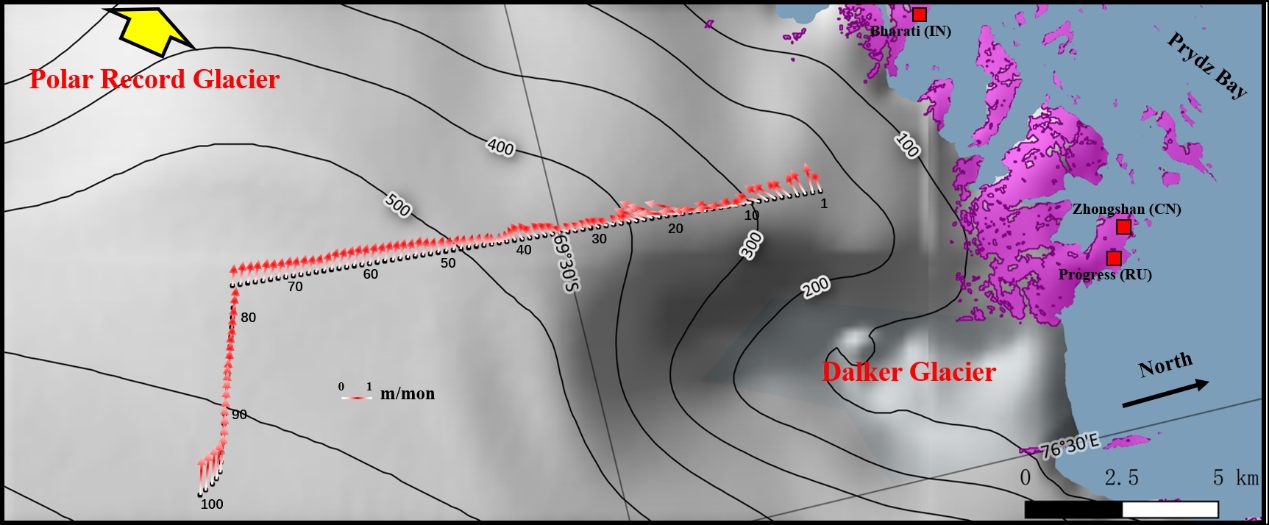
Figure 1. The ice velocity vector field in the Larsemann Hills. The direction and length of each red arrow represent the ice flow direction and monthly rate, respectively. The yellow arrow in the figure points to the Polar Record Glacier.
The first paper used the navigation-level GPS position information obtained during passive seismic observation to accurately track the movement characteristics of the ice sheet in the Larsemann Hills of East Antarctica and the Taishan station area. The group’s research results are of great significance for the study of ice sheet dynamics, glacier mass balance, and the evaluation of systematic errors caused by ice sheet flow in seismic imaging. This paper was published in Science China-Earth Sciences in July 2021. The first author is Dr. Fu Lei, and the corresponding author is Professor Xiaofei Chen.
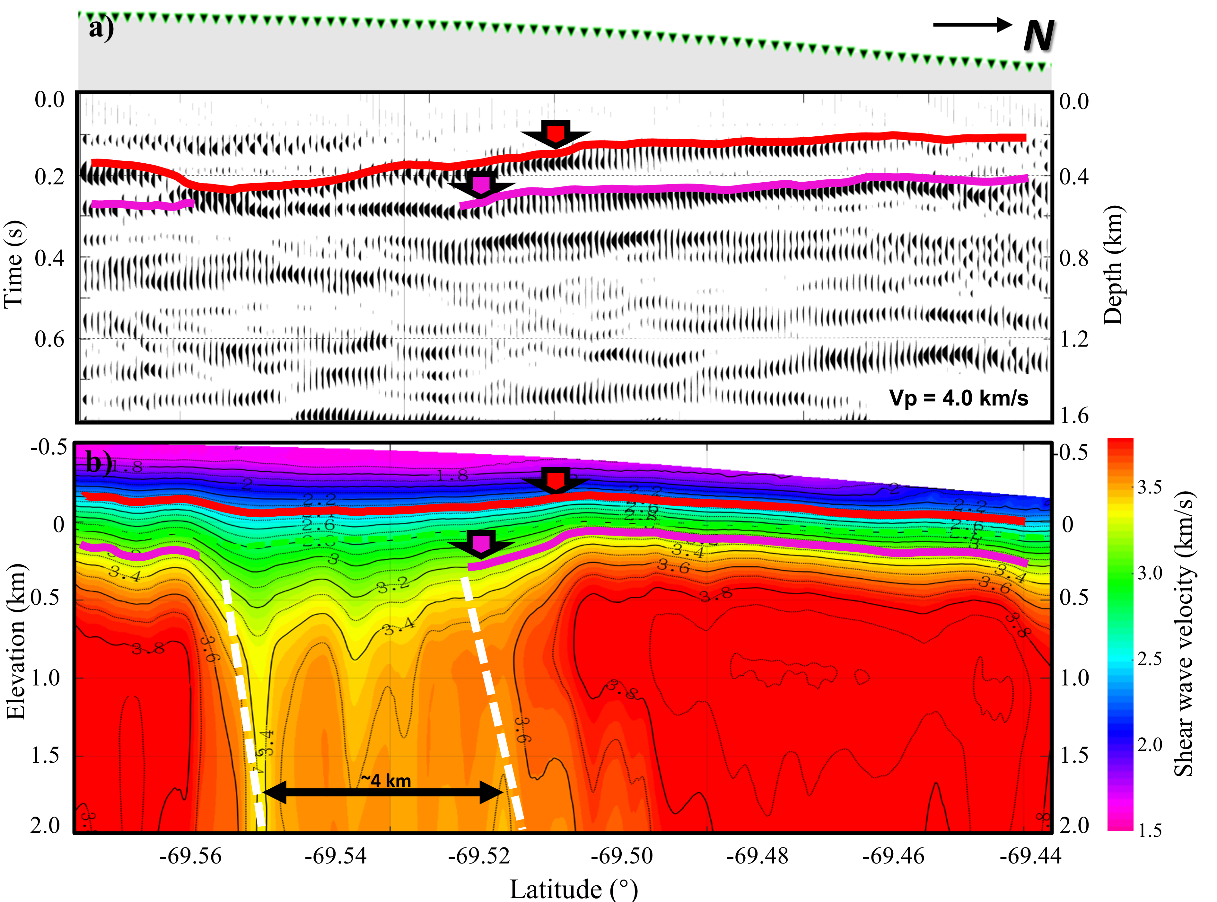
Figure 2. a) Stacked body wave image. The gray section on the top represents the ice sheet, where the surface elevation changes from 0.2 to 0.5 km. The green triangles represent the seismic stations deployed on top of the ice sheet. b) The shear wave velocity model from the inversion of dispersion curves.
The second paper uses the ambient noise data to image the ice sheet and upper crust structure. The Green’s functions of the station pairs are calculated with cross-correlation operations. The dispersion curves are extracted and inverted to obtain the fine shear-wave velocity structure of the ice sheet and the upper crust. At the same time, the stacked body wave image is migrated.
These research results provide the fine structure of the inner and upper crust of the Larsemann Hills ice sheet for the first time, which is of great significance for studying regional ice sheet dynamics and subglacial geology. The paper was published in Seismological Research Letter in September 2021. The first author is Dr. Fu Lei, and the corresponding author is Professor Xiaofei Chen.
Paper links:
Science China-Earth Sciences: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11430-021-9765-6
Seismological Research Letter: https://doi.org/10.1785/0220210135
By Lei FU
Proofread By Adrian Cremin, Yingying XIA



